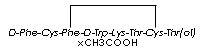|
OCTREOTIDE ACETATE |
| Synonyms. Octreotide acetate; D-Phenylalanyl-L-cysteinyl-L-phenylalanyl-D-tryptophyl-L-lysyl-L- threonyl-L- cysteinyl- L-threoninol cyclic (2-7)- disulfide acetate; Longastatin; Octreotida; Octreotide-LAR; Octreotidum; Sandostatin; Sandostatin LAR; 7-(4-Aminobutyl)-16-[(2-amino-3-phenyl propanoyl) amino]-13-benzyl-N- (1,3- dihydroxybutan -2-yl)- 4-(1-hydroxyethyl)-10-(1H-indol-3-ylmethyl) -3,6,9,12,15-pentaoxo-18,19- dithia- 2,5,8,11,14-pentazacycloicosane-1-carboxamide acetic acid; Phe-Cys-Phe-Trp-Lys-Thr-Cys-Thr-ol [Disulfide bridge: 2-7]; |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION | |
|
CAS RN |
83150-76-9(parent), 79517-01-4 (acetate) |
|
EINECS RN |
|
|
FORMULA |
C51H70N10O12S2 |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
1079.29 |
|
H.S CODE |
2933.99.7900 |
|
SMILES |
C(c1ccccc1)[C@@H]1NC(=O)[C@@H] (NC([C@@H](N)Cc2ccccc2)=O)CSSC[C@@H](NC([C@@H](NC([C@@H] (NC ([C@@H](NC1=O)Cc1c[nH]c2c1cccc2)=O)CCCCN)=O)[C@@H](O )C)=O) C(N[C@H](CO)[C@H](O)C)=O.CC(O)=O.CC(O)=O |
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Antineoplastic, Antisecretory, Gastrointestinal agent |
|
EXTRA NOTES |
A potent, long-acting synthetic SOMATOSTATIN octapeptide analog that inhibits secretion of growth hormone and is used to treat hormone-secreting tumors; diabetes mellitus; hypotension, orthostatic; hyperinsulinism; hypergastrinemia; and small bowel fistula. Somatostatin analog that is 3-times more potent than the native hormone in inhibiting the secretion of growth hormone. |
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
|
PHYSICAL STATE. |
white powder |
|
MELTING POINT |
|
|
BOILING POINT |
|
|
DENSITY |
|
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
Soluble (Soluble in acetic acid) |
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
log P(octanol-water) |
|
|
VAPOR PRESSURE |
|
|
AUTOIGNITION TEMP |
|
| pH |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions. |
|
INCOMPATIBLE MATERIALS |
Strong acids, Strong bases |
| POLYMERIZATION |
Has not been reported |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 0,Flammability:0, Reactivity: 0 |
|
|
| EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Octreotide is a hormone that occurs naturally in the body. It is used to treat carcinoid syndrome, which is seen in patients with carcinoid or neuroendocrine tumors. These tumors cause the body to overproduce certain hormones, and these hormones in turn can lead to symptoms collectively known as "carcinoid syndrome". Common symptoms include: flushing (90% of patients), diarrhea (75%), abdominal cramping (51%), and abnormalities of the heart valves (53%) possibly leading to right heart failure. Octreotide works to reduce the production of these hormones and thereby decrease the symptoms.
Octreotide is a synthetic octapeptide analogue with a similar pharmacologic action to that of somatostatin, but with a prolonged duration of action. It has a half-life of 100 minutes after subcutaneous administration. Its effects include the inhibition of the release of pituitary growth hormone and secretion of peptides (for example, insulin, glucagon, gastrin, and other peptides) and serotonin produced in the gastroenteropancreatic (GEP) endocrine system. It alters gastrointestinal motility, splanchnic blood flow, and gastrointestinal absorption. Somatostatin analogues have also been used in an attempt to suppress tumour growth through the inhibition of cell proliferation, stimulation of apoptosis, inhibition of the release of circulating tumour growthpromoting humoral effectors, and reduction in the blood supply to tumours. (http://www.cadth.ca/media/pdf/) The effect of Octreotide (SMS 201-995), synthetic somatostatin analogue on small intestinal and colonic fluid secretion induced respectively by cholera toxin (CT) and deoxycholic acid (DCA) was investigated in rabbits using in vivo isolated loops. After exposure to CT and DCA, marked fluid accumulation was observed in the small intestinal and colonic loops, along with elevation of jejunal and colonic mucosal cyclic AMP concentrations. Octreotide inhibited CT and DCA induced small intestinal and colonic secretion, dose-dependently. This anti-secretory effect was observed after both intramuscular and oral administration of octreotide. In contrast, octreotide did not affect the elevated mucosal cyclic AMP concentrations. These results suggest that octreotide inhibits CT and DCA induced intestinal secretion, and this anti-secretory effect is produced by affecting processes beyond cyclic AMP formation.(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) Gastric Antisecretory Agents
|
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
white to slightly yellowish powder |
| IDENTIFICATION |
pass (HPLC) |
|
PURITY |
98.0% min |
| AMINO ACID | ±10% (theoretical Composition) |
|
RELATED SUBSTANCES |
2.0% max (total impurity), 1.0% max (Individual impurity) |
| PEPTIDE CONTENT |
80.0%
min (N determination)
|
| ACETATE CONTENT |
15.0% max |
| WATER CONTENT | 8.0% max |
| OPTICAL ROTATION | -45.0° ~ -55.0°(c=0.5, 95% HAc) |
| BACTERIAL ENDOTOXINS | 5EU/mg max |
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION | |
|
UN NO. |
Not known |
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| PACKING GROUP | |
|
|
| SAFETY INFORMATION |
|
|
HAZARD OVERVIEW |
Not known |
| HAZARD CODES |
|
|
RISK PHRASES |
36 |
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
26 |
|
|
| PACKING |
|
|